Flipkart Business Model: How Flipkart Makes Money Working Explained

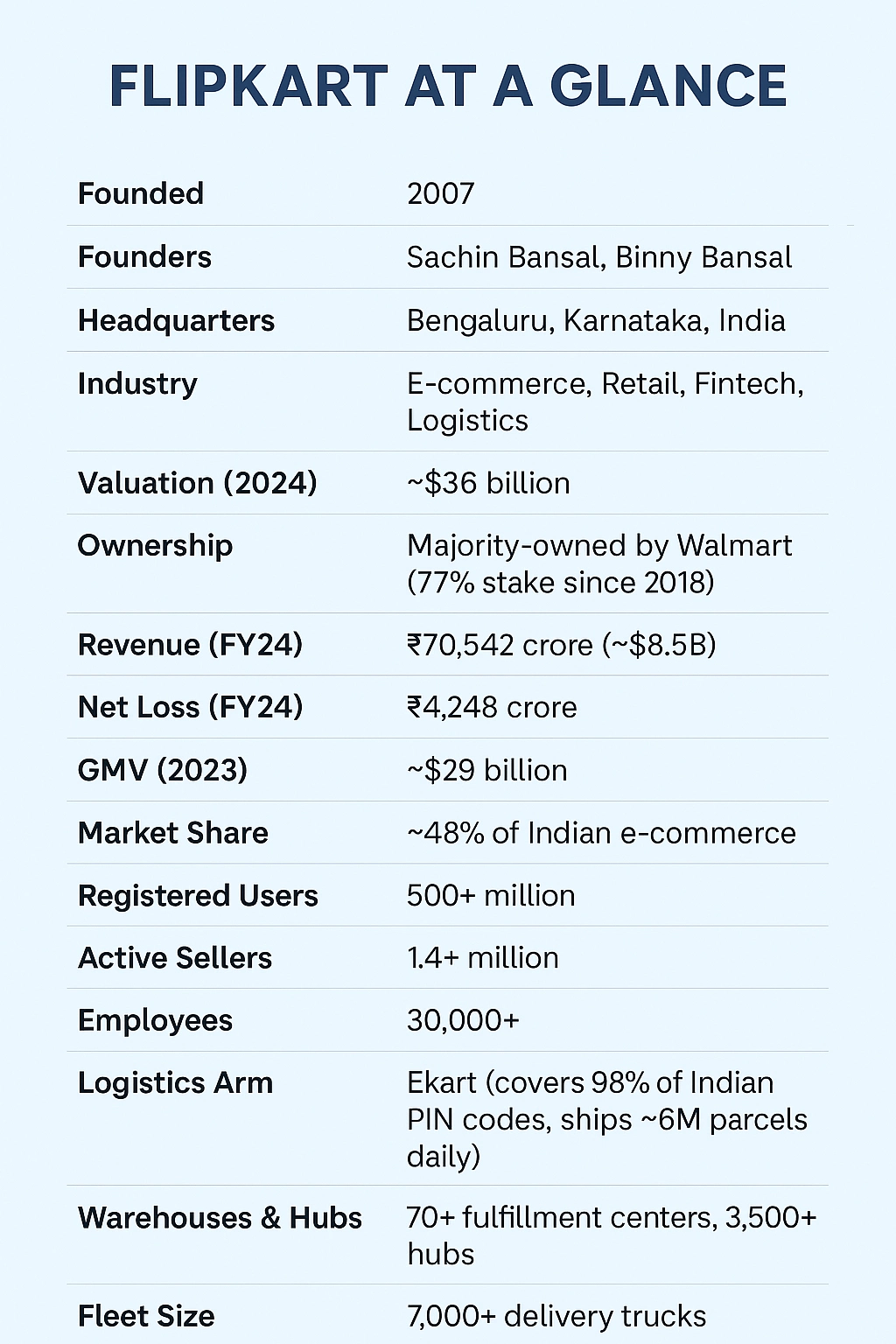
Flipkart is India’s leading homegrown e-commerce platform, founded in 2007 by Sachin and Binny Bansal. Now majority-owned by Walmart, Flipkart operates a comprehensive multi-service marketplace connecting over 1.4 million active sellers with more than 500 million registered users. It sells products ranging from books, electronics, and fashion to groceries by combining direct inventory sales with a vast third-party marketplace. Its business is built on a platform strategy driving revenue through product sales, commissions, advertising, fintech services, and fulfillment fees, supported by significant investments in logistics, technology, and customer acquisition.
In the fiercely competitive Indian market, Flipkart holds roughly 48% market share[1] as of FY2023, leading ahead of Amazon India (around 30–35%) and fast-growing social commerce players like Meesho.
How Flipkart Makes Money (Explained)
Flipkart’s core business model is that of a B2C online marketplace connecting millions of sellers to hundreds of millions of buyers across India. It blends direct retailing, third-party marketplace operations, advertising, and value-added services into a multi-layered revenue engine.
1. Revenue Streams
-
Direct Product Sales
Flipkart acts as a retailer for high-volume, fast-moving categories like smartphones, electronics, and appliances. By directly managing inventory in these segments, Flipkart ensures competitive pricing, high availability, and faster delivery. -
Marketplace Commissions
Over 1.4 million sellers list products on Flipkart’s marketplace. Flipkart charges commissions ranging from 5%–25% per transaction, depending on the category, creating a scalable revenue stream without holding all the risk of inventory. -
Advertising & Retail Media
Flipkart has built a fast-growing retail media business, selling promoted listings, banners, and data-driven ads to brands. This model, similar to Amazon’s retail media, generates high-margin revenue. -
Value-Added Services
Services beyond transactions increase customer stickiness:-
Ekart Fulfillment – warehousing, shipping, and reverse logistics.
-
Financial Products – EMI options, buy-now-pay-later, insurance.
-
Flipkart Plus – loyalty program offering faster delivery and partner rewards.
-
Convenience Features – COD, UPI integration, hassle-free returns.
-
Stat check: Flipkart Internet Pvt Ltd reported ₹70,542 crore (~$8.5B) gross revenue[2] (GMV) in FY2024, a 26% YoY increase. Net losses stood at ₹4,248 crore, highlighting high growth investments in infrastructure and customer acquisition.
2. Logistics & Supply Chain (Ekart Advantage)
Flipkart’s logistics backbone, Ekart, is its biggest competitive edge.
-
Infrastructure: 70+ fulfillment centers[3], 3,500+ hubs, 7,000+ trucks.
-
Scale: Over 6 million parcels delivered daily[4], covering 98% of India’s pin codes.
-
ONDC Integration: In 2025, Flipkart linked Ekart with the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), extending its logistics to third-party sellers beyond its marketplace.
This vertical integration allows Flipkart to control delivery experience, reduce costs, and monetize logistics as a standalone business.
3. Technology Infrastructure
Flipkart is as much a tech company as an e-commerce retailer.
-
Marketplace Scale: Supports 500M+ users, 1.4M sellers, 150M+ products.
-
Big Billion Day Traffic: Sales volume spikes up to 8× normal traffic.
-
Data Platform: Migrated to Google Cloud in 2024; processes 10PB batch + 2PB real-time data per day, with over 130B messages handled daily.
-
AI at Core: Powers personalized recommendations, demand forecasting, fraud detection, and dynamic pricing.
-
Flipkart Commerce Cloud (FCC): SaaS suite for global retailers, monetizing Flipkart’s tech stack beyond its marketplace.
4. Customer Acquisition & Experience
Flipkart invests heavily in festive sales, loyalty programs, and regional engagement.
-
Big Billion Day (BBD): Annual event since 2014, now a multi-day sales festival that drives billions in GMV. The first edition alone sold ~$100M in 10 hours.
-
Customer-Friendly Innovations: COD, no-cost EMI, easy returns, and UPI-first payments accelerated adoption in a price-sensitive market.
-
Flipkart Plus: Loyalty ecosystem tied with partner rewards to retain high-frequency buyers.
-
Localized Approach: Regional language interfaces and hyperlocal delivery (Flipkart Minutes) help reach semi-urban and rural India.
Result: Flipkart’s user base grew 21% in FY2023, outpacing Amazon India’s 13% growth.
How Flipkart Works (Step by Step)
To understand Flipkart’s business mechanics, here’s how the platform works in practice:
1. Seller Onboarding: Sellers register on Flipkart, list their products, and choose between self-shipping or Ekart fulfillment.
2. Product Discovery: Customers browse through categories on Flipkart’s app/website. AI-driven search and recommendation engines surface relevant products.
3. Transaction: Buyers place an order via COD, UPI, card, or EMI. Flipkart collects payment, deducts commission (if third-party seller), and remits the rest to sellers.
4. Fulfillment & Delivery: If Ekart-managed, products are picked from a warehouse, sorted at hubs, and delivered to customers often with real-time tracking.
5. Returns & Reverse Logistics: Easy return policies make Flipkart trusted among Indian buyers. Ekart also manages return shipments.
6. Monetization Beyond Sales: Ads, data insights, and premium services ensure Flipkart earns even without direct product sales.
Flipkart Vs Competitors: Amazon India and Meesho
Flipkart leads India's ecommerce market with about 48% share, while Amazon India holds around 30%, and Meesho rapidly grows with an estimated 15–20%. Flipkart has strong penetration in smaller cities and volume-oriented customers, while Amazon focuses on urban, premium shoppers through Amazon Prime, with more than 28 million Indian Prime members. Meesho operates as a social-commerce platform focusing on tier-2 and tier-3 cities, empowering micro-entrepreneurs with a zero-commission marketplace model.
In logistics, Flipkart’s Ekart network matches Amazon’s proprietary fleet and warehouse coverage, while Meesho relies on third-party courier services. Each platform has carved a distinctive niche: Flipkart leads in electronics and fashion, Amazon dominates tech-driven convenience and membership, and Meesho excels in social and mobile commerce.
Role of Technology and Data
Technology and data are at the heart of Flipkart’s operations. It uses AI and big data analytics to optimize pricing, forecast demand, manage inventory, personalize recommendations, and efficiently allocate marketing spend. The migration to Google Cloud has enabled Flipkart to process massive volumes of data daily and maintain platform reliability during sales spikes.
Flipkart’s proprietary analytics tools and SaaS products empower sellers and advertisers with data-driven insights, improving operational efficiency and customer experience. The platform continuously evolves these capabilities to sustain growth and competitive advantage.
Conclusion: Role of GrowthJockey
Flipkart’s model shows how scale, logistics, and technology drive India’s e-commerce growth. For emerging brands, replicating this playbook can be challenging. GrowthJockey steps in as a partner to bridge that gap offering AI-powered insights, market research, and operational support that help smaller sellers adopt strategies similar to large platforms, but in a way tailored to their scale.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does Flipkart generate revenue?
Flipkart earns revenue from direct product sales, commissions from third-party sellers, advertising, logistics fulfillment fees (via Ekart), and financial product services such as EMI processing and insurance. These combined streams helped drive a 26% revenue growth in FY2024.
2. What is Flipkart’s business model?
Flipkart is a B2C online marketplace facilitating transactions between buyers and sellers. It integrates retail operations, vast logistics, and a technology platform optimized for scale and customer convenience in India’s complex market.
3. How has Flipkart’s model evolved?
From its start as an online bookstore to a broad marketplace, Flipkart expanded via acquisitions (Myntra, Jabong), launched annual sales events (Big Billion Day), invested in technology and fintech (PhonePe), and broadened into wholesale, social commerce, and rapid delivery in recent years.
4. How does Flipkart compare to Amazon and Meesho?
Flipkart holds the largest market share (~48%) focusing on value and volume shoppers, Amazon targets urban and premium segments with Prime memberships, and Meesho leads social commerce in tier-2/3 towns with a zero-commission model.
5. What role does technology play?
Technology underpins Flipkart’s marketplace with big data and AI for demand forecasting, pricing, personalized marketing, and scalable cloud infrastructure. It enables seamless customer experience and efficient operations amid high transaction volumes and peak sales events.








