Project Mariner: Google DeepMind AI Web Browsing Agent Explained

Project Mariner is Google DeepMind’s experimental web‑browsing agent. Think of it as an assistant that doesn’t just answer questions - it does the work. Mariner can read what’s on your screen, plan the steps needed to achieve your goal and then carry out those steps in a browser. The agent can juggle multiple tasks at once and, after learning a workflow, can repeat it later with almost no prompting.
The big news in 2025 is that Mariner isn’t confined to the lab anymore. It’s powering new agentic features in Google Search’s AI Mode, helping with tasks like booking restaurant tables and finding event tickets.
Mariner itself remains in limited release via the high‑tier Google AI Ultra plan, but its capabilities are showing up in mainstream products. This article explains how Mariner works, what you can do with it today, and what comes next.
What is Project Mariner?
Project Mariner began life inside Google DeepMind as a research prototype exploring human‑agent interaction in the browser. Rather than provide information like a chatbot, Mariner is designed to perform tasks.
You describe what you need in natural language, and the agent opens a separate browser session, reads the page like you would, plans a series of steps and then clicks, types and scrolls to finish the job.
Google emphasises that Mariner is still experimental and currently available only to subscribers of the Google AI Ultra plan in the United States. However, its web‑browsing capabilities are powering new features in Google products.
At I/O 2025, Google announced that these agentic features will be integrated into the Gemini API and Vertex AI.
How Google Project Mariner Works: observe → plan → act
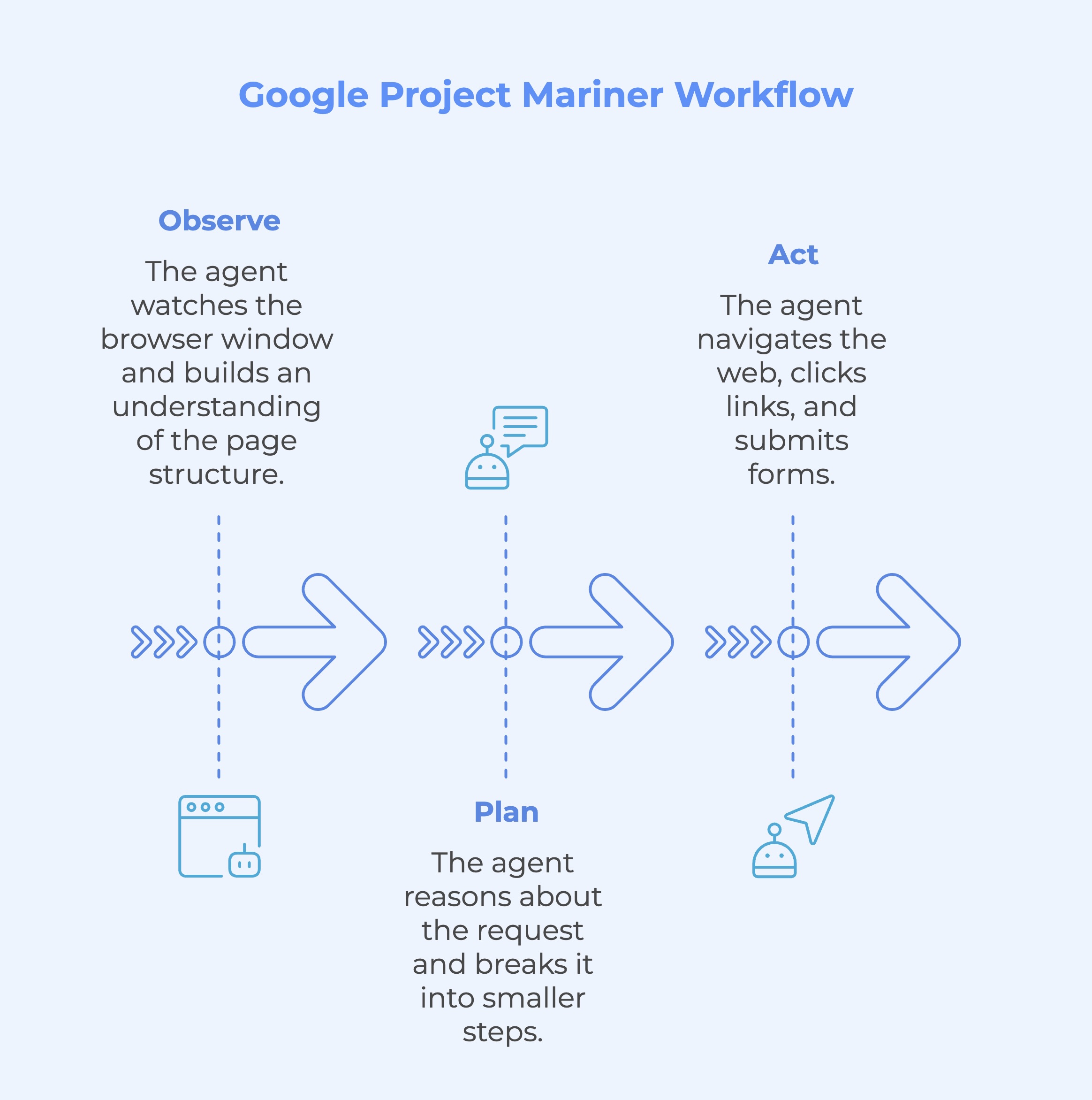
Mariner’s workflow mirrors how a human tackles a web task, but it does it autonomously:
-
Observe: The agent first watches the browser window, reading text, images, forms and even code. It builds an understanding of the page structure and the elements it needs to interact with.
-
Plan: Next, it reasons about your request, breaks it into smaller steps and shares a plan. This plan can involve multiple websites or stages, like filtering results, filling out forms and confirming selections.
-
Act: Finally, Mariner navigates the web, clicks links, types into fields, scrolls through pages and submits forms. You can watch its progress, intervene at any point or take over entirely.
Under the hood, Mariner runs each task inside an isolated virtual machine. This separation means you can assign up to ten tasks simultaneously without blocking your own browser.
Because each task runs in its own environment, you’re free to use your computer for other work while Mariner handles the chores.
Signature Capabilities of Mariner by Google
Mariner’s design gives it a few standout features:
-
Multimodal Understanding: The agent can parse text, images, buttons, forms and code on a web page. This allows it to navigate complex pages much like a person would.
-
Teach & Repeat: You can demonstrate a task once (for example, how you upload invoices to a vendor portal), and Mariner will learn that workflow. On future runs it can replicate the steps with minimal input.
-
Parallel Tasks: Thanks to its virtual‑machine architecture, Mariner can execute up to ten tasks at once. That’s useful for comparing prices across sites or gathering data from multiple sources concurrently.
-
Agentic Integration in Search and Gemini: Google’s AI Mode now uses Mariner’s live web‑browsing capabilities to handle actions like making restaurant reservations. These agentic tasks work with partners such as OpenTable, Resy, Tock and ticket sellers.
What You Can Do Today with Google Mariner?
Mariner is still evolving, but its current abilities are impressive. Here are a few early examples of how people are using it:
-
Book Tables or Tickets: Through AI Mode in Search, you can specify the party size, time, cuisine and location, and the system will search across reservation platforms to find available slots. It then takes you directly to the booking page so you can confirm the reservation.
-
Gather Information & Summarise: Assign Mariner to research a topic, compare products or find job listings. It will browse multiple sites, collect the necessary details and return a concise summary. Google’s demos show it finding personalised job postings and assembling research notes.
-
Automate Routine Workflows: By using the Teach & Repeat feature, businesses are automating repetitive portal tasks - uploading invoices, updating statuses or transferring data between systems.
-
Parallel Research Sprints: Because Mariner can run ten tasks at once, users are spinning up “agent tabs” to gather quotes, prices or vendor information from multiple sites concurrently.
These capabilities are just starting to appear outside the lab. According to Google, AI Mode is expanding from the U.S., India and the UK to more than 180 countries and territories in English.
The agentic features (like restaurant reservations) are initially available to AI Ultra subscribers in the U.S. via a Labs experiment.
Access, Rollout and Requirements
At present, direct access to Project Mariner is limited. Here’s what you need to know:
-
Plan Tiers: Mariner runs under the Google AI Ultra subscription plan, which costs $249.99 per month and includes priority access to Google’s most advanced AI models. Subscribers get early access to innovations like Mariner and Veo 3 video generation.
-
Geography: The research prototype is available only in the United States. Google says support for more countries is coming, but no timeline has been announced. However, features built on Mariner (such as agentic restaurant booking in AI Mode) are expanding globally through Search.
-
API Integration: Google is bringing Mariner’s computer‑use capabilities into the Gemini API and Vertex AI, allowing developers to build agentic workflows into their own applications.
Setup & Getting Started
If you’re in the U.S. and have a Google AI Ultra subscription, you can try Mariner via labs.google.com/mariner[1]. Here’s a general guide:
1. Launch a Task
Open the Mariner interface and describe your task in everyday language (e.g., “find three cheap flights from Delhi to Singapore next month”).
2. Watch the Live View
Mariner opens a separate browser session in a virtual machine. You can see what it’s doing and step in at any point to guide or stop the process.
3. Teach It
To use Teach & Repeat, download the associated Chrome extension and record yourself performing a workflow while narrating your steps. Mariner uses that recording as a template for future runs.
4. Review and Run
Edit the captured steps if needed. When you run the task again, Mariner will replicate your actions on the virtual machine, freeing you to focus on other work.
For agentic features in Search’s AI Mode, turn on the “Agentic capabilities in AI Mode” experiment in Google Labs if you’re an AI Ultra subscriber. Once enabled, you can issue complex requests - like booking a table under certain conditions - directly in the search box and let Google handle the heavy lifting.
Safety, Privacy and Controls
Google emphasises that Project Mariner is a research prototype and includes several safety measures:
-
User Oversight: Every Mariner session shows a live view and generates step‑by‑step logs. You can pause, resume or take over the browser at any point. Sensitive steps like entering passwords will prompt you to take over manually.
-
Permission Prompts: Because Mariner is still experimental, it only performs clicks, scrolls or typing in the active tab and always asks for final confirmation before taking sensitive actions, such as making a purchase. These prompts keep you in control, but they also introduce pauses as the agent waits for your approval.
-
Security Boundaries: Tasks run in virtual machines separated from your personal browser, and the agent uses only the data and accounts you explicitly allow. Google says it prioritises safety and security in developing these capabilities.
Despite these safeguards, reliability remains a concern. The agent isn’t always accurate and can be slow to complete tasks. Early reviews describe situations where Mariner loops through decisions or takes minutes to process simple forms.
External websites can block automation, CAPTCHAs may stop progress, and small interface changes may confuse the agent, so users must supervise and be ready to intervene.
Limitations & Open Questions
Project Mariner is promising but not yet polished. Areas to watch include:
1. Geographical and Pricing Barriers
Access is confined to U.S. AI Ultra subscribers. Even agentic features in Search currently require an Ultra plan for full functionality. It’s unclear when (or if) lower‑tier users or other countries will get direct access.
2. Automation Roadblocks
Mariner cannot bypass CAPTCHA challenges or one‑time passwords. Sites with strict anti‑bot measures may reject its actions. Complex flows with multiple confirmations often need human intervention.
3. Performance and Speed
Project Mariner remains a research prototype and is not always fast. Even Google notes that it can be slow and inaccurate today, and testers have found that processing simple forms can take minutes or the agent may get stuck in loops.
Frequent confirmation prompts also slow the flow but ensure that the user remains in control.
4. Data handling and Privacy
Questions remain about how credentials, cookies and tokens are managed inside the virtual machine, and how much data the system retains.
5. Global Rollout
Google has not shared a timeline for releasing Mariner outside the U.S., though its capabilities are appearing in products like AI Mode.
Google Project Mariner isn't Alone!
Mariner isn’t the only agentic system. OpenAI’s Operator, Anthropic’s Computer Use and Amazon’s Nova are also working on browser‑based agents.
Mariner’s strengths lie in Google’s distribution: integration with Search, Chrome and Gemini gives it a built‑in user base and access to partners like reservation and ticketing platforms. Its ability to run ten tasks concurrently and the Teach & Repeat feature help it stand out.
Use‑Case Playbooks
Below are some scenarios where Mariner’s strengths shine. These aren’t exhaustive but illustrate how the agent can be applied today or soon:
-
E‑commerce and Inventory Updates: Show Mariner how you list a product on your marketplace and it will replicate the process for dozens of items, saving hours.
-
Travel Planning: Let the agent run multiple tabs to gather flight options, hotel prices and car rentals, then summarise the best combinations.
-
Finance Ops: Record your monthly vendor portal workflow - download statements, upload invoices, reconcile balances - and let Mariner repeat it at month‑end.
-
Hiring and Recruiting: Use Mariner to search multiple job boards with specific criteria, scrape contact information and fill out applicant‑tracking systems.
-
Research Sprints: Assign tasks like “compare the top three CRM platforms”, "compare Amazon vs Flipkart" and “find five potential suppliers for aluminium tubing”; Mariner will return summaries with links and data points.
Final Thoughts
Project Mariner marks a shift from AI that advises to AI that acts. By observing, planning and executing tasks, Mariner promises to free people from mundane web chores. Early access remains limited, and the agent still struggles with complex flows and security hurdles.
But its integration into Google’s core products and the rapid expansion of AI Mode suggest that agentic browsing will soon be part of everyday life. As Google refines Mariner and broadens access, expect to see more workflows - from travel planning to finance operations - automated by an agent that understands the web like a human.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What can Project Mariner do?
Project Mariner lets Google’s agent see a web page, plan multi-step actions, and then act (click, type, scroll) under your approval. It can juggle multiple tasks in isolated sessions and powers action flows in AI Mode in Search (e.g., reservations/tickets via partners).
2. Is Project Mariner available in India?
AI Mode in Search expanded globally (English) on Aug 21, 2025, so India is covered; agentic booking flows roll out in phases and launched U.S.-first. You’ll experience Mariner inside Search/Gemini rather than as a standalone app; check Search settings → AI Mode.
3. What was the cost of Project Mariner?
There’s no separate “Mariner” price - early agent features have been tied to the U.S.-only Google AI Ultra plan (listed at $249.99/month). Pricing reflects the premium tier for early or advanced AI capabilities rather than a standalone Mariner product.
4. What impact did Mariner have on Google?
Mariner moved Google from answering to doing - fueling action flows in AI Mode and a task-oriented Agent Mode in Gemini. It underpins Google’s “agentic” direction, adds a premium on-ramp (AI Ultra), and reframes Search as a place to complete tasks, not just find links.
5. Is Project Mariner a separate app?
No. It’s a research prototype that powers agentic experiences in products like Search’s AI Mode and the Gemini API.
6. Can Mariner really run ten tasks at once?
Yes. Google says the agent can manage up to ten concurrent tasks in virtual machines.
7. Do I need an Ultra subscription?
Currently, yes. Mariner is available only to Google AI Ultra subscribers in the U.S. Agentic features in AI Mode also require this plan.
8. When will it launch outside the U.S.?
Google has not announced a timeline. However, AI Mode’s agentic features are expanding to over 180 countries in English.
9. Is it safe to let an AI fill out forms or make purchases?
Mariner shows a live view, logs its actions and asks for confirmation before sensitive steps. You retain control and can intervene at any time.








