Agentic AI vs Generative AI: Differences, Examples & Future Potential

Generative AI and agentic AI are two core parts of artificial intelligence, but they are quite different from each other. Generative AI listens to your instructions and produces output based on what you want. Agentic AI understands your goals and takes steps to get there independently. One reacts while the other initiates action. Together, they both help address creative and operational challenges in modern business.
Who would’ve thought we could talk to a machine and it would give us what we want back in seconds? Yet here we are, using generative AI to draft emails, design campaigns, and summarise hours of work with a single prompt. When it was introduced, it felt like magic, and now it has become the norm in every boardroom.
However, when it comes to artificial intelligence, the possibilities are constantly evolving. We're no longer just asking machines for output, but we're asking them to take action. That's basically agentic AI: following up with leads, filing reports, and adjusting our schedules.
But many teams are still confused between the two or assume they’re interchangeable. This blog breaks down the difference between generative AI and agentic AI, their unique features, and how they’re shaping the future of the business world.
Understanding the agentic AI and generative AI differences
Generative AI is the artificial intelligence that can come up with original content, such as images, video, audio, text, or code in response to the prompt you write. It works by identifying patterns across vast datasets and producing new outputs that match the intent, tone, or style requested.
Under the hood, generative AI relies on advanced machine learning models that mimic human pattern recognition to deliver output. While it's fast, flexible, and powerful for creation, it remains reactive, waiting for human instructions.
Agentic AI, on the other hand, is less of a creator and more of an executor. It doesn't just respond to your command but is designed to think ahead, take initiative, make decisions, and act on its own to achieve your outcome. Consider this: instead of asking it to write one email, you tell it to follow up with all your leads from last month, and it goes off to
-
Check your CRM
-
Identify who needs follow-up
-
Craft personalised messages
-
Send them out
As its name suggests, it acts independently like an agent to complete tasks by using natural language processing, machine learning, reinforcement learning, and knowledge representation.
Agentic AI vs Generative AI - at a glance
The table below shows the differences - outputs vs outcomes, prompts vs plans, and creation vs autonomous execution, so you can choose the right system for each use case.
| Dimension | Generative AI | Agentic AI | What does this mean for business |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core intent | Create content from patterns | Achieve goals via autonomous, multi-step action | One creates; the other acts. |
| Primary capability | Text, image, audio, and code generation | Planning, decision-making, tool use, execution | Use GenAI for outputs, Agentic AI for outcomes. |
| Autonomy | Reactive (waits for prompts) | Proactive (can initiate & continue tasks) | Agentic AI reduces manual supervision. |
| Reasoning & planning | Limited chain-of-thought; no explicit planning loop | Explicit goal-setting, planning, reflection, and replanning | Critical for workflows that span systems & time. |
| Memory & state | Short-lived conversation context | Long-lived memory, state tracking, episodic context | Agentic AI can “remember” and improve across runs. |
| Data freshness | Mostly static (unless paired with RAG) | Operates over live data streams & event triggers | Better for real-time ops (risk, ops, growth). |
| Best-fit use cases | Content, summarisation, code assist, design, and insights drafting | CRM follow-ups, ops automation, real-time monitoring, multi-app workflows, autonomous research | Creative vs. operational leverage. |
| Representative examples | ChatGPT, Midjourney, Stable Diffusion, Copilot | n8n-style systems, crewAI, LangGraph agents, enterprise agents (risk, ops, GTM) | Often combined in production. |
The feature breakdown: Agentic AI vs generative AI
Agentic and generative artificial intelligence both have different attributes that make them different from each other. Let’s take a look at them to understand which one would best suit your business needs.
1. Instructions and autonomy
Generative AI reacts to human prompts, processing the input it gets and producing output based on learned patterns. It performs your tasks as instructed but does not initiate actions or operate without external prompts.
Agentic AI demonstrates proactive behaviour by identifying potential actions without explicit instructions. These systems can recognise opportunities, suggest initiatives, and take steps toward goals with minimal human guidance.
So, generative AI requires clear instructions, whereas agentic systems can work towards larger goals and figure out how to achieve them independently.
2. Learning and adaptation
Once trained, generative AI models remain the same, and their abilities stay fixed unless they’re retrained with new data. They only change their responses based on different prompts, not as a result of learning during interactions.
Continuous learning mechanisms in agentic systems help them improve based on feedback and results. This adaptability allows them to refine strategies without full retraining.
3. Reasoning and planning
Generative AI excels at recognising patterns and producing outputs based on what it has learned, but it doesn't weigh different options or think through potential consequences. It simply generates content based on the most likely patterns from its training data.
Agentic AI approaches problems with a strategic mindset. It can evaluate multiple alternatives, consider various outcomes, and choose the best path forward. This allows it to navigate complex scenarios and execute multi-step strategies to achieve specific goals.
Learn how agentic reasoning enables AI to simulate outcomes before execution.
4. Feedback and interaction
Generative AI can adapt its outputs based on your feedback. If you don't like what it created, you can ask it to make changes, and it will adjust accordingly. However, it operates within a closed loop and can't sense or interpret what is happening around it or make changes on its own.
Thanks to its proactive nature, agentic AI actively engages with its environment, gathers relevant data and makes adjustments as situations change without waiting for your input.
Agentic AI and generative AI use cases: Where each artificial intelligence delivers the most business impact
While both technologies offer distinct capabilities, their real value lies in how they’re applied. The following use cases highlight where Agentic AI and Generative AI deliver the most impact for lean, fast-moving teams.
Generative AI use cases
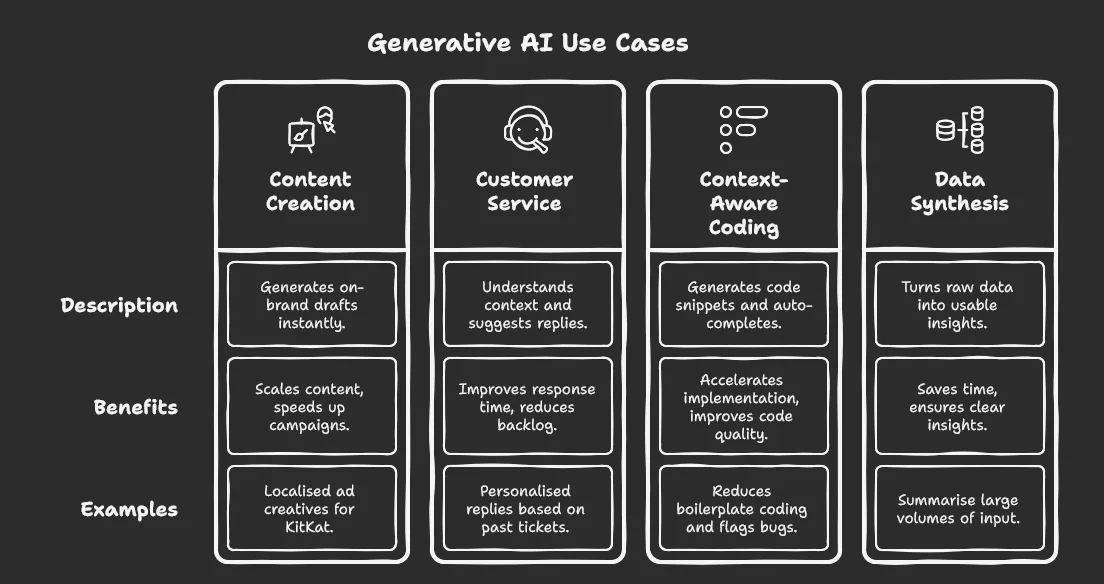
1. Content creation
Generative AI helps marketing teams scale content creation and speed up their campaign execution. Instead of writing each campaign email, ad copy, or product description manually, AI tools generate on-brand drafts instantly.
It also enables you to tailor messaging and visuals for different languages, cultural contexts, and audience segments. This is possible with models like GPT that understand tone, phrasing, and brand voice across markets.
Nestlé, for instance, used DALL·E to create localised ad creatives for KitKat and Nescafé campaigns, reducing turnaround time while maintaining brand consistency.
2. Customer service and support
Your customer service team can become overwhelmed with administrative tasks, making it difficult to respond to every customer quickly and consistently.
Generative AI, in the form of virtual assistants, helps by understanding context, suggesting replies, and even drafting complete responses during live interactions. These assistants help respond to customers in real-time, resolving queries quickly, reducing the backlog, and improving the customer satisfaction rate across every touchpoint.
Companies like Zendesk have already introduced generative tools that learn from past tickets and suggest personalised replies.
3. Context-aware coding
Generative AI helps generate context-aware code snippets, auto-complete functions, and even draft entire modules based on natural language input. This helps developers move faster on routine implementation tasks without getting pulled away from core architecture and design decisions.
Beyond writing code, these models also assist with translating code between languages, documenting logic flows, and suggesting improvements based on common patterns.
For instance, platforms like GitHub Copilot are already being used to reduce boilerplate coding and flag bugs in real time. This frees up engineering bandwidth and improves overall code quality with less manual effort.
4. Data synthesis and report generation
Generative AI is becoming a powerful tool for turning raw data into usable insights. It can analyse spreadsheets, dashboards, or meeting transcripts and generate summaries, trend explanations, or client-ready reports in natural language.
Instead of manually stitching together insights, teams can prompt the AI to write weekly performance summaries, board reports, or customer updates. Notion AI and Microsoft Copilot are already enabling teams to summarise large volumes of input, helping you save time and focus on decision-making.
This shift cuts down on tedious reporting cycles and ensures stakeholders get clear, contextual insights without the wait.
Agentic AI use cases
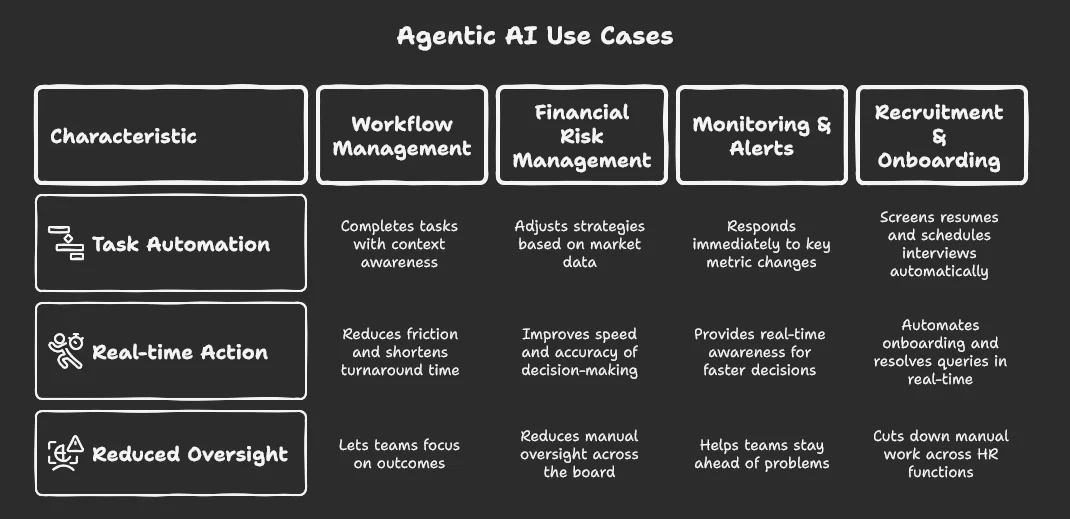
1. Automated workflow management across business functions
Agentic AI can now manage multi-step tasks across systems without constant human guidance. It doesn’t just suggest actions, but it completes them with context awareness.
For instance, it can scan your CRM, identify cold leads, write follow-ups, schedule emails, and track replies, all without manual coordination. Agentic AI can also apply the same logic to supply chain operations. It can flag stock delays, update supply levels, assign internal tickets, and notify the right teams based on pre-set logic.
This reduces friction between departments, shortens turnaround time, and lets teams focus on outcomes rather than micromanaging every step.
2. Real-time financial risk management
Agentic AI enables finance teams to manage risk dynamically by monitoring market data and adjusting strategies as economic conditions change in real time. It can evaluate interest rate shifts, credit exposure, or geopolitical events, then take action, whether by adjusting portfolio weights or flagging high-risk positions.
By acting in real time, these agentic AI systems help reduce manual oversight and improve the speed and accuracy of financial decision-making across the board.
3. Proactive monitoring and timely alerts
Agentic AI can track key business metrics like churn, revenue fluctuations, or engagement dips and respond immediately when something looks off. Instead of relying on reports to show up, agentic systems continuously monitor real-time data and take action, such as notifying relevant teams or suggesting next steps.
Take platforms like Intellsys. They centralise live data from multiple channels, generate targeted reports, and make suggestions to improve campaign performance.
This level of real-time awareness helps teams stay ahead of problems and make faster, smarter decisions across operations, marketing, and product.
4. Smarter recruitment and seamless onboarding
Agentic AI can streamline hiring by screening resumes, sending personalised messages to candidates, and scheduling interviews without human coordination.
Some enterprise teams also use agentic tools to automate onboarding journeys, resolve IT or HR queries in real-time, and track task completion without requiring manager follow-ups. This cuts down manual work across HR functions, speeds up onboarding, and ensures new hires get quick access to tools, resources, and support from their first day.
Top 3 emerging trends in agentic and generative AI
The future of artificial intelligence is evolving fast, with different trends shaping how this technology will be developed, deployed, and scaled across industries. Let’s take a look at these agentic AI and generative AI trends:
1. Integration and hybrid systems
The line between generative and agentic AI is blurring as developers combine their strengths into hybrid systems. These systems use generative abilities for creating content and responses, while adding agentic features for reasoning and independent actions.
Rather than seeing them as separate tracks, developers are building layered frameworks where generative AI handles creative or language tasks inside broader agentic workflows.
For example, OpenAI’s GPT-based agents now combine code generation with execution, allowing the system to solve problems, write scripts, and run calculations without constant human input.
2. Specialisation by domain
Both technologies are shifting away from general-purpose use and toward domain-specific optimisation. This involves designing AI with built-in industry logic, data standards, and regulatory awareness.
In sectors such as healthcare, finance, legal, and manufacturing, these tailored systems are outperforming general models by focusing on their scope. For example, AI in radiology now interprets scans using medical context, while AI in banking factors in KYC norms and real-time credit risk signals.
This specialisation is making AI more usable, safer, and aligned with industry needs.
3. Responsible AI development
With growing concerns around safety and control, both agentic and generative systems are being rebuilt with transparency, traceability, and ethical regulations as core priorities.
The focus is shifting toward making AI decisions explainable, particularly when systems operate independently. This means building in audit trails, establishing clear model boundaries, and creating flexible autonomy levels that allow humans to step in when needed.
Developers are also embedding ethical constraints from the ground up to prevent biased decisions, hallucinated outputs, and unchecked automation in sensitive environments.
Quick chooser: when to use which?
| Situation | Pick Generative AI when… | Pick Agentic AI when… | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Goal | You need high-quality outputs (text, code, visuals) | You need goals achieved end-to-end with minimal human nudging | |
| Scope | Single prompt → single output | Multi-step workflows across tools, teams, or time | |
| Latency | Instant insight or draft is fine | System must monitor, decide, and act in real time | |
| Data | Mostly static or summarisation-heavy | Live data, streaming events, constantly changing context | |
| Risk & control | Low-risk experimentation or creativity | High-stakes ops that demand auditability & guardrails | |
| Team maturity | You’re early in your AI journey | You can support observability, sandboxing, and human-in-the-loop |
Concluding thoughts: Agentic AI vs generative AI
The difference between agentic AI vs generative AI goes beyond technical terms. It signals a shift in how businesses automate, scale, and delegate thinking.
Generative AI helps teams create faster. Agentic AI helps systems think ahead, take initiative, and adapt over time. That’s a fundamental change in how work gets done.
The edge lies in combining them - using generative tools to create and an agentic system to execute. It’s not about replacing people but about building smarter workflows that run with less input.
At GrowthJockey, we act as your full-stack venture architect, helping you identify, access, and implement the right AI solutions to accelerate growth. From maximising revenue to reducing operational costs, we make AI work for your business goals.
You'll also gain access to our proprietary platform, Intellsys.ai, which automates workflows, analyses real-time data, and enables smarter decision-making at scale.
If you’re ready to explore what AI can do for you, reach out to see how we can help.
FAQs on agentic AI vs generative AI
1. What is the difference between AGI and agentic AI?
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) refers to theoretical systems that can match human intelligence across all domains, with broad reasoning and adaptive learning. Agentic AI, on the other hand, is a practical technology. It can operate autonomously within defined boundaries to execute tasks, make decisions, and adapt based on the feedback it receives.
2. Is agentic AI part of generative AI?
No, they are separate but often complementary. Generative AI focuses on creating content like text, images, or code based on learned patterns. Agentic AI, meanwhile, is built to act independently, take actions, and carry out multi-step tasks. Many agentic systems integrate generative models to handle content generation within larger workflows.
3. What is the difference between agentic AI and ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is a generative AI system built for conversation and content generation. It responds to prompts but doesn’t act beyond what it’s asked. Agentic AI systems, in contrast, can maintain goals, plan across steps, and take independent action like initiating follow-ups, coordinating tasks, or adapting to live inputs.
4. Can agentic AI make decisions without human input?
Yes, that’s one of its core capabilities. Agentic AI can evaluate context, prioritise actions, and adjust workflows without waiting for human instructions. It follows defined objectives but navigates decisions independently, whether it’s responding to changes in market data or resolving support tickets.
5. Which is better: agentic AI or generative AI?
There is no correct answer for this. It depends on the outcome you’re aiming for. Generative AI is best for content-focused tasks like writing, designing, coding, or summarising information from large datasets. Agentic AI is ideal for planning and automating tasks like sending follow-ups, assigning responsibilities, managing workflows, or monitoring in real-time.








