Agentic AI in Insurance: Benefits, Strategy, Use Cases

The insurance industry has never been an easy one.
You're constantly dealing with high-stress situations, accidents, property damage, and health emergencies. Every case is urgent, and every detail matters. When systems are slow or manual, it doesn't just create delays; it creates frustration, cost overruns, and lost trust.
The reality is that many insurers still rely on processes that can’t keep up. Claims take days or weeks. Underwriting decisions are buried under paperwork.
Scaling with this setup is almost impossible, and with customer expectations getting higher by the day, the pressure is only growing.
This is where agentic AI is starting to make a real impact.
Unlike traditional AI, which typically needs human oversight, agentic AI is designed to act independently. It can process claims, detect fraud, personalise support, and even make complex decisions without constant human intervention.
In this blog, we’ll explore how agentic AI is changing the way insurance companies operate. This includes automated claims processing, AI-powered fraud detection, intelligent underwriting systems, and personalised customer experiences.
Let’s see what this new era of insurance looks like and how businesses can keep up.
What Happens Inside An Insurance AI Agent: 6 Simple Steps
Understanding how agentic AI in insurance works doesn’t have to be complicated. Fundamentally, these systems function as intelligent, self-sufficient assistants, observing, making decisions, and taking actions independently.
Here's what that process looks like in practice:
Step 1: Constant monitoring
Every autonomous insurance agent is always “on.” It tracks real-time data, from claim activity, policy updates, and customer behaviour to external risk indicators.
Think of it like a radar that never blinks. It’s not waiting for a human to prompt it. It’s proactively watching for signals that something needs to happen.
Step 2: Understanding context
When a trigger is detected - say, a new claim or a policy change request - the agent doesn’t just follow a script. It reads the data, checks historical records, identifies patterns, and applies logic to determine what's actually happening.
This is where agent-based decision making kicks in. The system weighs options and makes informed choices using the same logic a human would but faster, and at scale.
Step 3: Taking action (autonomously)
Once it has the context, the agent acts.
In automated claims processing, this might involve verifying the policy, cross-checking supporting documents, and automatically approving low-risk claims.
In insurance policy automation, it may adjust coverage levels or update premium terms, eliminating the need for manual input.
Low-risk claims often clear instantly because the engine uses a knowledge-based agent to match rules with past precedents.
Agents only loop in humans when a situation is too complex, too rare, or flagged as high-risk.
Step 4: Collaboration across system
These AI agents aren’t working in isolation. They’re integrated into a larger automation framework.
They coordinate with tools used in intelligent underwriting systems, plug into CRMs, and sync with analytics platforms. So, whether it's a claim, an onboarding step, or a fraud flag, it all connects.
This cross-team coordination reduces bottlenecks and speeds up resolution time. Smooth hand-offs rely on tight workflow orchestration with agentic AI.
Step 5: Learning and improving
Each time an agent handles a case, it learns. Not just from outcomes, but from how old cases were resolved, what led to human intervention, and how decisions impacted risk.
That feeds directly into better risk modelling in insurance and sharper personalised insurance recommendations over time. That feedback loop mirrors a live agentic RAG retrieval layer pulling new data before each decision.
Step 6: Full traceability and compliance
Every action taken, automated or not, is recorded.
That means if an AI tool approves a claim, flags a fraud risk, or updates customer info, there's always a clear log of what happened, when, and why.
This is especially important in insurance, where staying compliant and audit-ready isn’t optional.
3 Reasons Why Insurers Are Adopting Agentic AI
Agentic AI in insurance is fixing things that have been broken for years. We're talking faster operations, smarter decisions, and customers who actually feel understood.
Here’s what that looks like in action:
1. Claims get settled in hours
Waiting weeks to settle a claim is exhausting for customers and insurers. That’s where automated claims processing powered by agentic AI makes a huge difference.
These systems don’t wait for someone to review documents or chase down approvals. They verify if the policy covers the claim, review photos and estimates, and calculate the payout - all on their own.
They also flag anything unusual for a human to double-check, keeping the process clean and compliant.
HDFC ERGO cut claim settlement time for motor insurance from 15 days to just 2 hours. Their system handled photos, estimates, police reports, all while syncing up with garages and surveyors. They massively cut costs and witnessed a 40% jump in customer satisfaction.
2. Risk decisions are sharper and more accurate
Traditional risk assessment relied on surface-level data like age, income, maybe some health info.
Now, agentic systems dig deeper.
Using intelligent underwriting systems, they evaluate everything from credit scores and health records to behavioural patterns and even digital footprints.
Let’s see Max Life Insurance’s example, where they built a system named MediCheck. It automatically scans lifestyle and medical histories, flags high-risk profiles with 85% accuracy, and instantly approves low-risk ones.
They learn from past claims, spot patterns in real time, and constantly refine their models to improve accuracy. This led to cost-cutting and much better risk selection across the board.
3. Customer service is more personalised
Most insurance services feel robotic, even when they’re run by people. But with AI-driven customer onboarding and support, you get the opposite.
Agentic systems remember what a customer asked last time. They know when to reach out, how to speak, and what products might actually help.
It’s automation and personalised insurance recommendations at scale.
ICICI Lombard nailed this with a system named RIA that adapts its customer chats based on their identity and history.
It suggests products they might actually need. It predicts questions before they’re asked. And it has helped them keep more customers around while cutting down on support volume. It’s a textbook case of agent assist in AI raising retention without increasing head-count.
3 key Use Cases Where Agentic AI is Making a Difference Today
Let’s break down where agentic AI in insurance is actually doing the heavy lifting today.
We’re not talking about future potential but real, high-impact applications already reshaping core operations.
Here are three key use cases making a clear difference:
| Application | How it works | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| Automated claims handling | Agents manage the full claims process - validating coverage, analysing. This involves managing damage, coordinating with repair networks, and settling payouts. | Cuts down manual review time, accelerates automated claims processing, and improves consistency at scale. |
| Fraud detection and prevention | Tracks behavioural patterns, documents timing, and external data sources to flag suspicious activity in real-time. | Strengthens AI-powered fraud detection, reduces false positives, and protects against rising fraud threats. |
| Customer onboarding automation | Guides new customers through personalised policy selection, data collection, and form completion while ensuring compliance. | Powers smooth AI-driven customer onboarding, boosts conversion, and reduces drop-offs. |
Check out more real-world agentic AI examples in our curated guide
Adopting Agentic AI in Insurance: A Practical Rollout Strategy
Adopting agentic AI in insurance requires more than just a simple switch.
It’s a step-by-step process that balances tech, people, and regulation, because without structure, even the smartest AI will not work.
Here’s how to roll it out the right way:
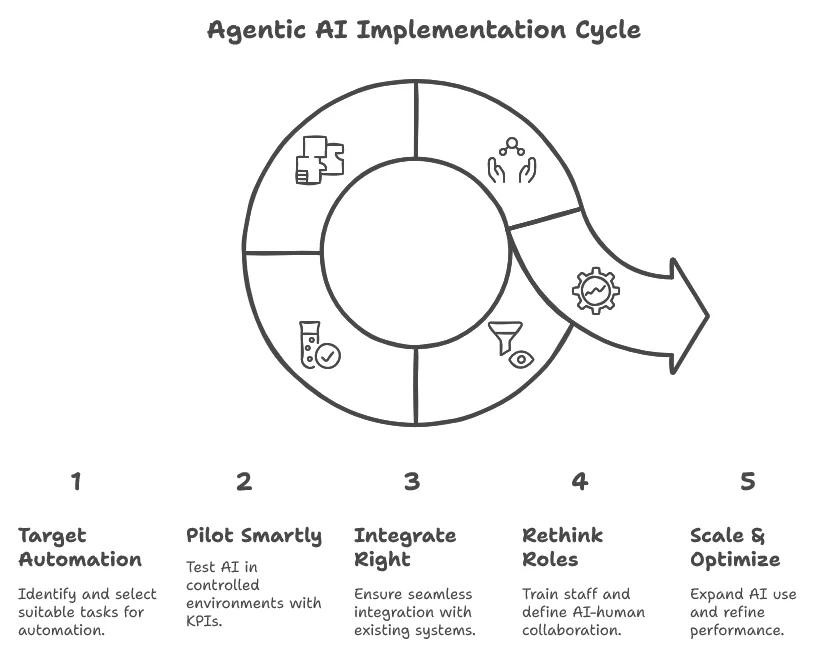
1. Pinpoint high-impact, low-risk automation targets
Start with a detailed audit of operational workflows.
Look for high-volume, low-complexity processes with predictable outcomes, such as FNOL (First Notice of Loss), document verification, or standard customer queries.
Make sure you evaluate:
-
Process maturity
-
Quality and accessibility of data
-
Regulatory conditions (e.g., where human oversight is mandatory)
-
Integration feasibility with existing platforms
These areas are where agent-based decision making can deliver fast ROI with minimal disruption.
2. Design focused pilots around measurable outcomes
Avoid broad, open-ended experiments.
Instead, define 1–2 specific use cases, like automated claims processing for minor motor damage or AI-assisted onboarding for term life customers.
Set clear KPIs from the start:
-
Reduction in handling time
-
Accuracy of decision-making
-
Escalation rate to human agents
-
Customer satisfaction improvement
Keep pilots contained within one region, product line, or team. The goal isn’t just to test the tech. It’s to validate how well AI agents operate in a live business setting.
3. Choose AI tools that fit your core tech
Many insurers encounter difficulties during implementation. They attempt to incorporate AI without harmonising it with their primary systems.
When integrating next-gen insurance AI tools, ensure:
-
APIs allow real-time data flow between core systems (policy admin, CRM, claims)
-
Data security and compliance standards are met (e.g., audit trails, GDPR/IRDAI compliance)
-
Agents can operate across functions – claims, underwriting, and service – without creating silos
This is essential when connecting functions like intelligent underwriting systems, AI-powered fraud detection, and insurance policy automation.
4. Redesign roles, not just train people
Training is more than just about learning the tool. Employees should understand:
-
Where autonomous insurance agents take over (e.g., low-risk, rule-based tasks)
-
When and why is escalation to a human-triggered
-
How human oversight complements AI decision-making
Clear guardrails come from human-in-the-loop approval systems that log every override. This clarity reduces fear of “replacement” and shifts focus to collaboration, especially in complex use cases like risk modelling in insurance or exception handling.
Consider creating “AI-human partnership roles” focused on reviewing AI decisions, refining inputs, and managing exceptions.
5. Scale gradually, optimise continuously
Once pilots succeed, avoid rushing a full rollout.
Instead, expand by:
-
Adding new use cases (e.g., moving from claims to underwriting or support)
-
Broadening to new product lines or geographies
-
Introducing more advanced agents for personalised insurance recommendations or proactive retention
Build in continuous feedback loops between business units and AI teams. Use dashboards to monitor model performance, customer experience, and compliance risks in real time.
Make optimisation a monthly and not an annual exercise.
The Future of Insurance Isn’t Just Automated - It’s Agentic
Agentic AI in insurance isn’t just another wave of automation.
These systems handle what used to drain time and resources - routine claims, risk checks, and customer onboarding. But the real opportunity isn’t just in speed or cost savings.
It’s in redefining how insurers operate, make decisions, and serve people.
Of course, this shift comes with trade-offs. There’s still a need for human oversight, governance, and a clear ethical framework. That’s where most insurers struggle - not with the technology itself, but with how to embed it in real workflows, teams, and compliance-heavy environments.
As a startup accelerator in india, we work with insurers to make that transition practical. We help build agentic solutions that deliver results and hold up under regulatory pressure.
Now, the big question isn’t “Should we use AI agents?”
It’s: How do we make AI part of the business without losing the human judgement, ethics, and trust that insurance is built on?
The next insurance era will be defined by how wisely we use tools and tech.
FAQs On Agentic AI In Insurance
1. How is agentic AI different from traditional insurance automation?
Traditional RPA follows fixed rules and stops when data fall outside templates. Agentic AI monitors context in real time, makes its own decisions, and escalates only edge cases, cutting cycle times from days to hours.
2. Can AI really approve an insurance claim without human review?
Yes, when policy terms, damage estimates, and risk scores all fall inside preset thresholds, autonomous agents can validate. It can pay low-risk claims instantly while logging every step for audit.
3. How does agentic AI detect fraud in real time?
Multiple specialised agents watch behaviour, device ID, location, and spend history at once. When combined signals cross a risk score, the system blocks the transaction and flags a human investigator.
4. What are the compliance risks of autonomous insurance agents?
The main risks are opaque decision logic and data-privacy breaches. Mitigation requires explainable models, immutable audit logs, and human-override workflows aligned with IRDAI and GDPR rules.








